
Source: Cacycle [CC BY-SA 3.0]
DMT is the chemical component found in the ayahuasca infusion, a drink with potent psychoactive properties used by the native peoples inhabiting the Amazon in South America.
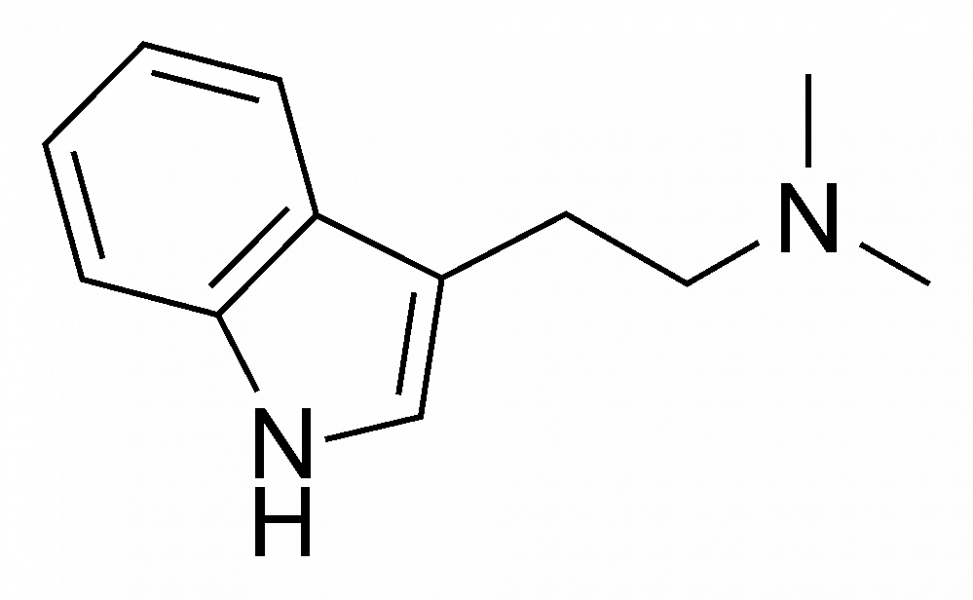
The substance is a tryptamine derivative under the name N,N Dimethyltryptamine with the chemical formula C12H16N2. It was synthesized in 1931 by Canadian chemist Richard Manske and in 1946 a Brazilian microbiologist named Oswaldo Gonzalvez discovered that it is a natural alkaloid found in several plants.
In 1953, a Hungarian physicist and chemist named Stephen SzáraThe study of the substance and its role in mental illnesses, relationship with serotonin, sleep phases, extraordinary functions of the brain and its effects on consciousness will be studied in depth from then on.
In the 1970s, ayahuasca tourism began in Amazonian countries such as Peru, Brazil and Colombia, and the dissemination of the use of this ancestral preparation was the subject of worldwide studies.
Its use is related to its ability to regulate the Sigma – 1 receptor of the central nervous system, this protein is found in various tissues of the body and is related to cardiovascular function, depression, addictive behaviors and schizophrenia.
How DMT is consumed
The substance extracted from various plants has been synthesized to be consumed in various ways, smoked, injected, snorted in pure DMT crystals or ingested in capsules of DMT-based organic salts but the preferred consumption is by drinking the infusion of the indigenous tribes of the Amazon known as Ayahuasca.
Ayahuasca is obtained from the mixture of a plant rich in DMT content as the chacruna (Psychotria viridis) and the vine Banisteripsis caapi, which has the alkaloid Harmalina that is responsible for inhibiting the enzyme monoamidoxidase or MAOI, This enzyme reacts with the metabolism of tryptamine and dopamine, thus increasing the concentration of these neurotransmitters and preventing monoamine oxidase or Mao from degrading DMT.
DMT and its component N,N Dimethyltryptamine, is also found in other plants such as chagropanga (Diploterys cabrerana) and jurema roots, which are often used in shamanic rituals, as well as in our own brains and those of rodents in a natural way. By inhibiting the enzyme monoamine oxidase, DMT can act with a greater intensity and in a longer period of time, causing psychoactive reactions that vary depending on each person.
Effects of DMT
The main effects of DMT on the organism include a different perception of reality, which leads to experience an opening of consciousness, visions of parallel worlds where they can meet their ancestors or other lives. Unwanted effects include negative or frightening hallucinations and increased blood pressure, vomiting and diarrhea due to the purgative effect of the infusion.
The psychic effects of the substance are manifested in an altered state of consciousness where different visions of a cosmic and mythological nature are experienced, followed by a state of introspection with a high emotional charge where the experience is reflected upon.
A recurrent effect of DMT administration is synesthesia, which translates as the sensation of hearing colors or seeing music. As for hallucinations or visual phenomena, they are characterized by geometric and kaleidoscopic shapes, jungle animals or mythological or supernatural beings.
DMT, which is produced naturally by the brain, is attributed to the visual effects of dreams, near-death experiences and spiritual experiences. In studies conducted by the Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry at the University of Kuopio in Finland, it was determined that DMT levels are elevated during the visual sleep phase which produces the hallucinations experienced in dreams or nightmares.

DMT considerations
In 1971, the Single Convention on Psychotropic Substances considered DMT to be a banned chemical with no therapeutic value, so that in some countries its use is prohibited even for scientific research. In some South American countries its use is permitted for use in traditional shamanic ceremonies.
DMT is naturally present in the brain, therefore its prohibition would apply to the synthesized version but not to the endogenous one. This substance offers an invaluable opportunity in human and natural pharmacopoeia for the development of knowledge on multiple scales and is therefore considered a research resource on a scientific and metaphysical level.
N,N Dimethyltryptamine and other serotonergic substances have demonstrated their efficacy as a treatment to heal multiple mental pathologies such as anxiety, depression, post-traumatic stress disorders and to control recreational drug addictions.
DMT has been purported to be linked to recreational drugs but due to its potency and impact on the physical, emotional and spiritual levels it is incomparable to any of these substances. The possibilities it offers are profound and supremely broad as it can not only channel a therapeutic or healing use, religious and psychedelic experience but is seen as a combination of all these experiences.
Sources
http://www.onirogenia.com/lecturas/analogos-de-la-ayahuasca-jonathan-ott.pdf
(S/f-b). Onirogenia.com. Retrieved June 20, 2022, from http://www.onirogenia.com/lecturas/analogos-de-la-ayahuasca-jonathan-ott.pdf.
Santos, R. G. D. (2007). AYAHUASCA: neurochemistry and pharmacology. SMAD. Revista eletrônica saúde mental alcool e drogas, 3(1), 00-00.
View of Ayahuasca: the meeting of two paradigms. (n/d). Edu.pe. Retrieved June 20, 2022, from https://revistas.upch.edu.pe/index.php/RNP/article/view/1162/1194.
Di Bella, G. (2020, February 5). Cerimônias com ayahuasca levam xamanismo indígena à metropole. National Geographic. https://www.nationalgeographicbrasil.com/cultura/2020/02/cerimonias-com-ayahuasca-levam-xamanismo-indigena-metropole
(S/f). Academia.edu. Retrieved June 20, 2022, from https://www.academia.edu/download/63206133/DMT_Alcaloide__Espiritu_Sagrado_-_Ali_Cortina_202020200505-85841-18zovmy.pdf.
Strassman, Rick. DMT: The Spirit Molecule: A Doctor’s Revolutionary Research into the Biology of Near-Death and Mystical Experiences. Rochester, Vt.: Park Street, 2001.

Gerson Alvarado, Comunicador Social egresado de la ULA Táchira, Venezuela. Actualmente desempeñando funciones de Comunicador y Reportero Audiovisual. Fotógrafo, Músico y Ciclista. Apasionado por captar imágenes de paisajes y documentar historias.
This post is also available in:
![]() Español (Spanish)
Español (Spanish)
